Many have called Ethereum “the next bitcoin”, which can be both correct and incorrect. In many ways, Ethereum is a more ambitious project than bitcoin. Which is also the reason why many speculate, whether their money would be better invested in an Ethereum project, rather than Bitcoin, or whether both are worth investing in.
| At eToro you can trade 49 currency pairs, including several cryptocurrencies. Join eToro |
Ethereum is a decentralised platform for applications, that makes it possible to run programs on it without the risk of fraud, censorship, downtime or interference from a third party.
The project also includes the cryptocurrency ether, the second largest cryptocurrency in the world. Since Ethereum (ether) is the second-most known cryptocurrency, it would make sense to have it in the portfolio. It’s easy to exchange Bitcoin for Ethereum, therefore it is common to assume that a small part of bitcoin’s high volume will in time flow into ether. In 2017 Bitcoin was introduced as futures on multiple exchanges. And as for number 2, ether can be next in line to be announced as a future, which may lead to several Ethereum price increases in 2018.
Here’s an overview of what you should about Ethereum and ether cryptocurrency:
How to buy Ethereum (ether)?
The easy way: that’s how you buy ether via a contract
Why buy ether?
Who’s behind Ethereum?
What is ether’s exchange rate?
How to buy ether with a wallet?
How to buy Ethereum (ether)?
Ethereum cryptocurrency trades on a long list of platforms across the world.
There are basically two ways to trade ether.
1. The easy way: speculating on the price of ether via a contract that follows prices of cryptocurrencies
2. Buying ether and opening a so-called wallet to store it (more difficult)
If you solely wish to speculate on price developments, and not actually use ether to buy anything, then we recommend to simply buy a contract, where price developments are followed – this has a long list of advantages. Among other things, you don’t have to figure out how to open a “wallet” and other technical subtleties that come from owning ether.
| At eToro you can trade 49 currency pairs, including several cryptocurrencies. Join eToro |
The easy way: how to buy ether via a contract
Trading a cryptocurrency like ether via a contract has a number of advantages. First, you don’t have to figure out what it means to have a wallet and other technical details that result from owning ether. Second, you have the possibility to trade on an exchange that is subject to EU’s financial law, which gives you rights as a consumer. Third, if the exchange you trade on goes bust, you want to be sure that you’re covered and can get your money again, up to a certain amount at least. At the time of writing (May 2018) you are covered up to 20.000 euros. While there are some exchanges that offer such insurance, the new Bitcoin exchanges, where you actually trade and own cryptocurrencies, offer no such option.
Another problem – bitcoin exchanges are very vulnerable to hacks. If one happens, you run the risk of losing all your money. Back in 2014, the world’s biggest bitcoin-exchange at the time, Mt. Gox, was hacked, and close to 460 million dollars of customer’s money disappeared into thin air. Many exchanges have been hacked since. South Korean Youbit exchange went bust after a hack stole around half a billion dollars in late 2017. Another hack rocked a Japanese Coincheck exchange in January this year. Stolen NEM tokens were worth nearly half a billion dollars. The hack’s size and the impact were often compared to that of Mt. Gox, sparking new discussions about the security of cryptocurrency exchanges.
If you don’t use your ether for anything, but merely wish to speculate on the price using a contract, we don’t recommend going out and buying real ether. You get exactly the same value increase with a contract – without the risk of trading on an unregulated exchange.
Why buy ether
At this point in time, ether has the position as number 2 on the cryptocurrency hierarchy ladder. But it’s not only Ethereum’s reputation as “the next bitcoin” that makes it interesting. Ethereum can be much more than bitcoin.
Ethereum was launched in 2015 with the idea of giving users the possibility to build “decentralised applications”, where you can pay with ether to buy computing power on the computers that are run by members of the network. These applications can be everything from financial services to a simple game. And everything is run in a way that makes it impossible for a centralised authority to shut it down.
This provides a number of possibilities. Since Ethereum is run fully decentralised, the project is often described as the invention of the “world’s computer”, and the combined computing power can solve a lot of new problems.
Many businesses are now working to offer a decentralised backup-solution based on Ethereum’s technology, so in the future, you can use a backup that is 90% cheaper than the one you get with Google or Amazon – among others, Storj is working on that. This is possible because one can rent free space on their hard drive and store a fraction of another computer’s file, which is constructed from file fragments from other computers. However, the entire file can only be assembled by the computer that originally made the backup.
Here is a video that shows an overview of ideas behind Ethereum
Like bitcoin, Ethereum is based on blockchain technology, and Ethereum has built on this by inventing “smart contracts” – a good example of how all types of contracts can be translated into computer code and automatically executed when a particular condition is met.
Let us take an example: Let’s imagine that you own a hairdressing salon, and you ask an online marketing company to optimise your website so that it shows on the first page of Google when one searches for “Hairdresser in my city” two months later. The company says that they can fulfil the task at the cost of 10 ether if successful, and 2 ether otherwise. Then they get to work.
Normally, you would first send a contract, sign it, and when the job is done, the supplier would ask for money. He would then sign an invoice that you then send to the accounting department, and the supplier may or may not receive his money 30 days later.
With a “smart contract” you set a simple rule via a program: then check if the website is listed as a number 1 result for “Hairdresser in my city” two months later – if that’s the case, transfer 10 ether. Otherwise, transfer 2 ether.
In this way, you will experience that contracts can be settled without friction or delays. And the company that has developed a specific “smart contract” based on Ethereum can be paid a little fee for its trouble, perhaps 0,0001 ether. And in this way, a new, more efficient economy is invented.
| At eToro you can trade 49 currency pairs, including several cryptocurrencies. Join eToro |
Who’s behind Ethereum?
Ethereum was founded by Vitalik Buterin, Jeffrey Wilcke and Gavin Wood. Three years ago they came to Zug, Switzerland, also known as “crypto valley” due to numerous crypto-companies that have started their business in the city. Their goal was to build next-generation blockchain technology by building “Ethereum world computer” and programmable “smart contracts”.
Many thought that the project was too ambitious. But it turned out that they underestimated the brain power that had come to town.
Later in the year, Ethereum carried out a so-called ICO (cryptocurrency exchange listing), which brought them 18,4 million dollars to finance the project. At that point, the price of ether sat well below a dollar, but in 2017 alone the value rose over 7000%. One of the founders, Vitalik Buterin, is thought to be worth more than 2 billion dollars, a lot of it in ether. He stores his 60-number encryption code in one place only, his head. If he forgets the code, the money is lost.

Ethereum has a strong team behind it. The founder Vitalik Buterin is a good leader of the Ethereum community. It’s of great value to a community to have a leader that can show the way. Compared to for example bitcoin, where nobody knows what happened to its creator Satoshi Nakamoto, and therefore the power is shared between different groups.
Ethereum is a more scalable technology than bitcoin but has had some problems with scaling itself. Have you heard of “Crypto Kitties”? It’s a game where you can buy, sell, and trade crypto kittens. The game got so popular that it nearly brought the Ethereum network down, which called Ethereum’s scalability into question.
Despite this, it is likely that the big Ethereum community will solve these problems, and since Ethereum will be introduced to more exchanges in 2018, there may be several price increases ahead.
On the other hand, there is naturally the risk that Bitcoin, or another cryptocurrency, may be in a massive price bubble, and if bitcoin starts to drastically fall, it can also affect Ethereum. It makes sense, therefore, to see Ethereum as a long-term investment. In 10 years the cryptocurrency can be worth either 0 or many times more what it is worth now. You can follow those prices with coinmarket.com – or see them below:
Ethereum – US Dollar exchange rate
How to buy ether with a wallet
If you chose to buy “the easy way”, you don’t have to read the rest of the text, as it focuses on what to do if you want to buy actual ether and store it on a wallet. When you read the following description, it will become clear for you how challenging it may be to buy ether.
Before you buy ether it is important to familiarise oneself with how a “wallet” works. Both its transactions and its software. When you buy actual cryptocurrency, there is no mercy. If you make a simple mistake, you can lose everything on your account. However, this risk can be reduced, if you approach the situation with caution, and follow the guide below.
An Ethereum wallet is a piece of software that stores value you have in ether. Ethereum wallets can be an application that runs on your computer, on a phone as an app, or as so-called “hardware wallet” or an online exchange. The official Ethereum wallet can be downloaded at Ethereum.org.
If you want to buy Ethereum and secure your money, you should download a wallet. Here you can choose between a “light client” or a “full node”. If buying ether is new for you, then we recommend you to download the light-version, as the “full node” downloads the whole Ethereum blockchain, which takes several gigabytes.
Here are links to light-version wallets:
MyEtherWallet
Jaxx.io
The latter also supports other cryptocurrencies.
What is a private key?
After you have chosen an Ethereum wallet, you will get a private key. This is the key to your wallet. If someone else gets hold of it, they will have full access to your wallet and all your money on it. When you create your wallet, you will be asked to make a copy of your private key. The wallets that we linked above generate a key offline, that is never sent to a server, and therefore is impossible to be captured by others. The way you store your key is up to you. There were, unfortunately, examples of users, who forgot what they have done with their private key. And if that happens, there is no way to get it back again. The money on your wallet is gone.
Some users have chosen to print their private key and store it offline. If you have a big amount of ether, you can choose to get a hardware wallet, as described below.
Transactions and addresses
When you have downloaded your wallet and secured your private key, it time to transfer money. But before you start, you should be familiar with how a simple ether transaction looks like. Your wallet will automatically generate a number of recipient addresses, known as so-called “public keys”, and unlike the private key, these can be distributed without risk. Payments to these addresses will be sent to your wallet. All transactions on the Ethereum blockchain are visible through a “block explorer”, such as etherscan.io.
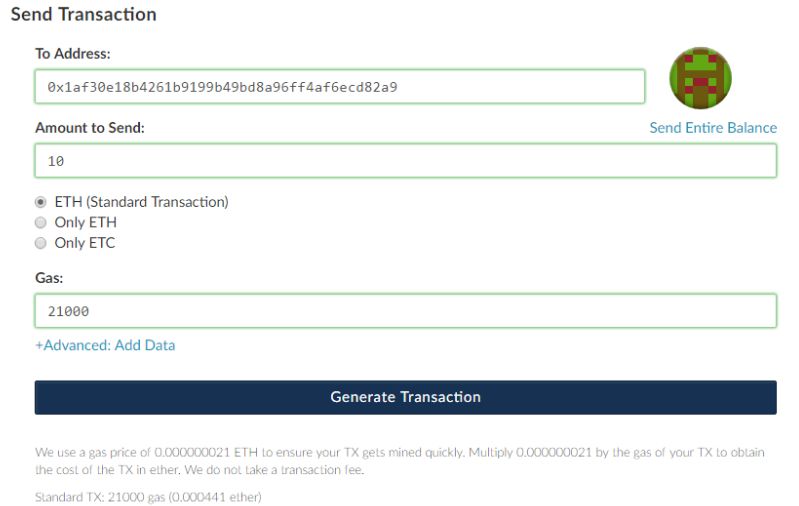
This is a transaction of 10 ether. First, you input the address of the person you wish to make a payment to, then the amount, and the so-called gas, which is the transaction fee. The fee amount will usually be given during the transaction process, either in ether or dollars. The fee is determined automatically based on the wallet software you use.
When the transaction is completed, it will be written into the blockchain. It will be then confirmed by computers around the world. It will become more and more integrated, and when it is confirmed over 30 times, it will be considered extremely secure and will stay on the blockchain forever.
The same principles follow when you receive a transaction. If you want to buy ether, the exchange where you want to buy it will ask for your wallet address. In the beginning, while the transaction is being confirmed by computers all over the world, it will be seen as “pending” in your wallet.
How to transact safely
Although it happens rarely, there have been a number of horror stories about people who lost thousands of dollars because of a mistake while making a transfer. Here are a few things you should be aware of:
- Copy-paste the wallet address. Never write it yourself. The address is long and includes both small and big letter, and a single mistake will result in loss of your money forever. There is no option to transfer the money back, and Ethereum has no customer support number to call.
- Check the transaction fee. A good wallet will show the fee amount in dollars and cents. Always check if the amount is reasonable.
- Double check the address. When you have copy-pasted the address you want to send the ether to, check it again and again, until you’re sure that it is correct. If you look at the first and last digits, you can make sure that it was copied correctly.
- A good wallet will also confirm the address that you send to. This reduces the risk of a malware detecting and replacing the recipient address.
We also encourage you to try and carry out a test transaction. One of the driving forces behind Ethereum is low transaction fees. Therefore, it might be a good idea to send a small amount of ether to test your understanding of the process and make sure that you grasp all the details. This will ensure that everything goes as it should when you send a bigger amount.
How to secure your ether (the easy, but less secure way)
If you want a simple way to secure your ether, you can entrust it to the exchange where you trade it. However, this poses some risk concerning the platform. As said earlier, when Mt Gox got hacked, the users lost close to half a billion dollars. There is also the risk of digital theft, as exemplified by Bitfinex.
Despite this, some users choose to leave large sums of ether or bitcoin with the exchange and let them secure it. But when you choose to do this, there is no possibility of securing the money yourself. You should consider how much you trust in the exchange you trade on, and how much currency you are willing to entrust them.
If you have smaller amounts on a cryptocurrency exchange compared to your overall investment volume, you could consider leaving the money with the exchange. But when you store the money on an exchange, you don’t get a private key. This also means that you pass responsibility for your ether to the exchange. You should also be aware that cryptocurrency exchanges are not the same as a bank, and are not regulated under the same financial legislation. Should an exchange go bankrupt, you may lose all your money.
| At eToro you can trade 49 currency pairs, including several cryptocurrencies. Join eToro |
How to secure your ether (the hard and secure way)
Hardware wallets are one of the safest ways to secure your ether. They can generate and store your private key offline, and under no circumstances will they be exposed to an internet-connected computer or phone. If you store cryptocurrencies offline, you decrease the risk of digital theft – one of the biggest risks for people investing in cryptocurrencies.
When a device is used, it creates a recovery key, and you can choose a PIN. Both parts must be protected well, as any unauthorised access may lead to you losing your money. Two of the most respected hardware wallets for cryptocurrencies are Trezor and Ledger Nano S.
Two-factor identification
You can also protect yourself further with the help of two-factor identification and multi-signature wallets. When you store ether on an exchange, or in a form of a wallet, two-factor identification acts as a good additional protection. The process ensures that the user enters a one-time password before logging into his waller and sending ether. Google Authenticator is one of the most used for this purpose and is used by many Ethereum wallets. This additional protection means that a potential thief must not only have your password but also have access to for example your mobile, in order to receive the one-time password that has been generated.
It is very secure to use an app such as Google Authenticator. A number of other platforms choose to send you a one-time password via SMS. This should be avoided, as in many cases the password can be seen without opening the phone.
You can also choose to use multi-signature wallets. These wallets allow users to secure their ether by letting multiple users sign every transaction. Typically, you must use 2 out of 3 private keys to sign a transaction. The 3 private keys can be stored in various physical places so that one cannot access them from a single place.
Which level of security you choose is up to your tolerance for risk. Securing cryptocurrencies is an area under constant development. And if you have a wallet, you should ask the company which methods they recommend.
As can be seen, it may be a somewhat troublesome and technical process to buy ether as a cryptocurrency. Therefore, we recommend speculating on the price via a contract using one of the various trading platforms.











